5G – the fifth generation of mobile wireless technology – is much faster than 4G and able to deliver speeds of over 1 Gbps. In addition, it has much lower latency. It is the next generation of mobile technology and is already available on all the three major US carriers.
But not all 5G is the same. For example, there are three different broad types available:
- Low-band 5G has maximum speeds that are just a little better than 4G, but it covers longer distances and so is more suitable for less built-up areas. This is the type of 5G that is mostly available in the USA.
- Mid-band 5G has much faster speeds than low-band 5G, but it doesn’t broadcast far and so requires more infrastructure to deliver. Mid-band 5G delivers speeds that are up to 10 times faster than 4G. This is the type of 5G that the rest of the world is mostly deploying.
- Millimeter-wave 5G only works in contained areas (like buildings or stadiums) but it is super-fast, and is the version that is capable of delivering 1 Gbps speeds.
How fast a carrier’s 5G service is depends on which type of 5G they have deployed at that location, so in practice, your 5G connection will not be much faster than 4G speeds if your carrier is using Low-band 5G. Expect speeds of between 200 and 500 Mbps from Low-band 5G networks.
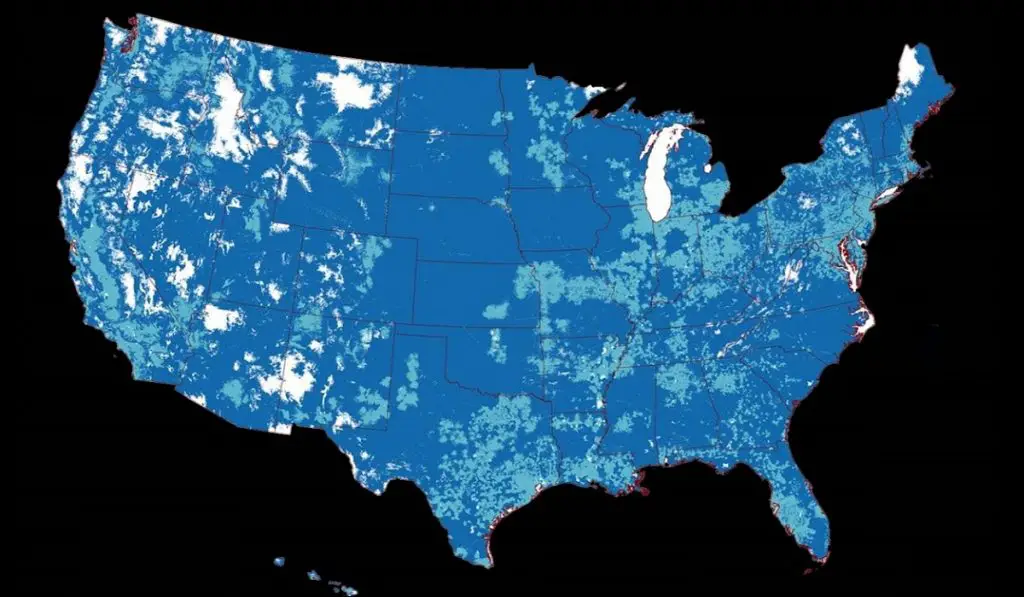
Which wireless carriers have 5G in the United States?
All three major carriers – AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile – have 5G service across the United States, but coverage is far from total at this time. As a matter of fact, we are still in early days in 2021. Some of their MVNOs – smaller carriers that use the towers and cell sites of the major ones – also already offer 5G cellular service as well.
T-Mobile currently has the widest 5G coverage in the country. The carrier runs Low-band, Mid-band, and mmWave 5G networks. Mid-band 5G was widely used by Sprint and got transferred to T-Mobile as a result of the acquisition, giving the carrier an edge in its deployment and currently has the largest Mid-band coverage.
It calls Low-band service by the term “Extended Range 5G” and its Mid-Band and mmWave services go by the term “Ultra Capacity 5G“.
Verizon runs Low-band and mmWave 5G networks, with the former taking a huge chunk of its coverage. This carrier markets its Low-band services as “Nationwide 5G“. Its faster but smaller millimeter-wave 5G network is branded as “5G Ultra Wideband” or “5G UWB.”
AT&T has Low-band and mmWave 5G networks, also with Low-band being the much wider technology. The carrier uses the terms 5GE, 5G and 5G Plus in its marketing, but 5GE is not really 5G; just a rebranded 4G service, while its “5G” service refers to its regular Low-band and Mid-band 5G services. The term “5G Plus” is used for its mmWave service.
At this time, 5G cellular service is available to about 300 million subscribers across the three major carriers. All carriers are constantly expanding their 5G service.
To confirm 5G coverage at your location, check out your carrier’s 5G coverage map on their website, as follows:
Check out T-Mobile’s 5G coverage map, Verizon’s 5G coverage map, and AT&T’s 5G coverage map.